Upper GI & Biliary Diseases
Gall stones
 Gallstones or cholelithiasis, the condition in which gallbladder is filled with stones are increasingly becoming common. Majority of the patients with gall bladder stones are not even aware of the condition and come to know of the condition on screening ultrasound of the abdomen. Gallstones form due to loss of gallbladder contractility and over-saturation of bile. The primary reasons for above include irregular timing of meals, refined foods with high fat content and lack of regular exercise. They are more frequently seen in women, especially during or after pregnancy.
Gallstones or cholelithiasis, the condition in which gallbladder is filled with stones are increasingly becoming common. Majority of the patients with gall bladder stones are not even aware of the condition and come to know of the condition on screening ultrasound of the abdomen. Gallstones form due to loss of gallbladder contractility and over-saturation of bile. The primary reasons for above include irregular timing of meals, refined foods with high fat content and lack of regular exercise. They are more frequently seen in women, especially during or after pregnancy.
Symptoms can appear in the form of pain or indigestion. People usually complain of pain at night or after meals. Some patients complain of bloating or indigestion regularly after meals. These symptoms are often ignored initially and some patients directly present with complications of gall stones like jaundice and pancreatitis. Patients at high risk of complications include patients on immuno-suppressive medications, stone size more than 3 cm or uncontrolled diabetes. Complications of gallstones include
- Acute Cholecystitis, when patients present with continuous excruciating pain and features of infection like fever and breathlessness
- Bile duct stones, when the stones slip into bile duct and cause jaundice
- Acute pancreatitis, which is the most severe complication.
Gallstones need treatment when they are symptomatic or at risk of complications. Treatment for gall stones is entirely surgical since there are no effective medicines for the dissolution of stones. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is the standard of care for treating gall stones. Unlike renal stones, the problem lies with the non functioning gall bladder. Hence removal or dissolution of the stones does not cure the patient. Also there are no effective scientifically proven medicines for dissolution of the gall stones.
Important facts:
- Gallstones treatment includes removal of gallbladder along with stones. Removing stones alone is not performed since neither symptoms nor complications are related to stones alone.
- Removal of gallbladder does not damage digestion since it is not essential for digestion in the first place.
Peptic Ulcer
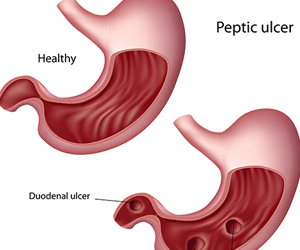 Peptic ulcer disease involves a spectrum of conditions from complicated ulcers with bleeding to milder erosions and non-ulcer dyspepsia. The primary problem involves increased gastric acid secretion and weakened protective layer in the stomach. The main reasons for these include
Peptic ulcer disease involves a spectrum of conditions from complicated ulcers with bleeding to milder erosions and non-ulcer dyspepsia. The primary problem involves increased gastric acid secretion and weakened protective layer in the stomach. The main reasons for these include
- Helicobacter pylori infection: This is the bacteria highly prevalent in south India. This spreads to contaminated water or food.
- Excessive use of NSAIDs: These are the common pain killers like ibuprofen or diclofenac which are used for headache or body/ menstrual pains
- Food additives: Usage of unapproved coloring agents and lime in fast-food can irritate the stomach.
Majority of patients complain of upper abdominal pain/ burning sensation with bloating sensation. Patients with deep ulcers sometimes present with backache, vomiting and dark coloured stools. When untreated these can develop into complicated ulcers which include
- Perforation: The ulcer ruptures leading to sudden onset of severe abdominal pain and features of infection which can be life threatening. This needs emergency surgery for closure of the ruptured ulcer.
- Bleeding: This can vary from mild bleeding and diagnosed as anemia to massive episodes of blood vomiting. This needs emergency endoscopy for control of bleed or surgery if endoscopy is unsuccessful.
- Gastric obstruction: Patients with long standing ulcer disease develop scarring and narrowing of stomach. This leads to frequent vomiting and inability to eat. This also needs endoscopic dilatation in mild cases to surgical correction in complete obstruction.
With better medicines to cure H pylori and suppress the acid secretion (proton pump inhibitors like pantoprazole), surgery is rarely ever needed nowadays when this condition is diagnosed early. Simple and effective steps like use of clean drinking water (RO filtered/ mineral), reducing usage of NSAIDs (pain medicines), and avoiding foods with synthetic additives help in reducing the risk of developing acid peptic disease.
- Peptic ulcer disease is completely curable and should not need life long medication.
- Long term use of acid suppressing medicines like PPI (Pantoprazole) can be harmful.
GERD
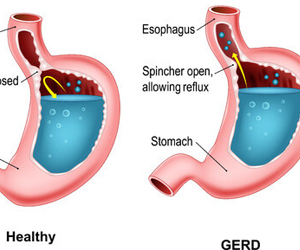 Gastroesophageal reflux disease is the condition which arises when excessive acid and gastric juices regurgitate into the esophagus. The gastroesophageal valve which is a one directional valve allowing free passage of food but preventing acid reflux is weakened due to various reasons, among which presence of hiatus hernia and life style related stresses are the most important.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is the condition which arises when excessive acid and gastric juices regurgitate into the esophagus. The gastroesophageal valve which is a one directional valve allowing free passage of food but preventing acid reflux is weakened due to various reasons, among which presence of hiatus hernia and life style related stresses are the most important.
Patients usually feel what is typically called as heartburn, a burning sensation in the middle of the chest. Some patients feel squeezing pain or bitter sensation in the throat, especially while lying down. Some patients can develop atypical symptoms like foul breath, cough or dental discoloration due to the refluxed gastric acid. Long standing reflux can lead to complications like
Stricture: narrowing of the food pipe leading to inability to swallow.
Bleeding: Ulcers in food pipe can present with blood stained vomiting.
Barretts’ esophagus: Long exposure to acid and digestive juices damage the innermost lining of the food pipe called as mucosa. This leads to Barretts’ esophagus which can predispose to cancers.
Majority of patients, when diagnosed early can be cured with life style changes (explained in Health tips section) and /or medications. Those patients who have long standing reflux needing regular medicines or those with severe or complicated GERD benefit from a one-time anti reflux surgery performed laparoscopically. The basic principle involves the strengthening of the gastroesophageal valve.
